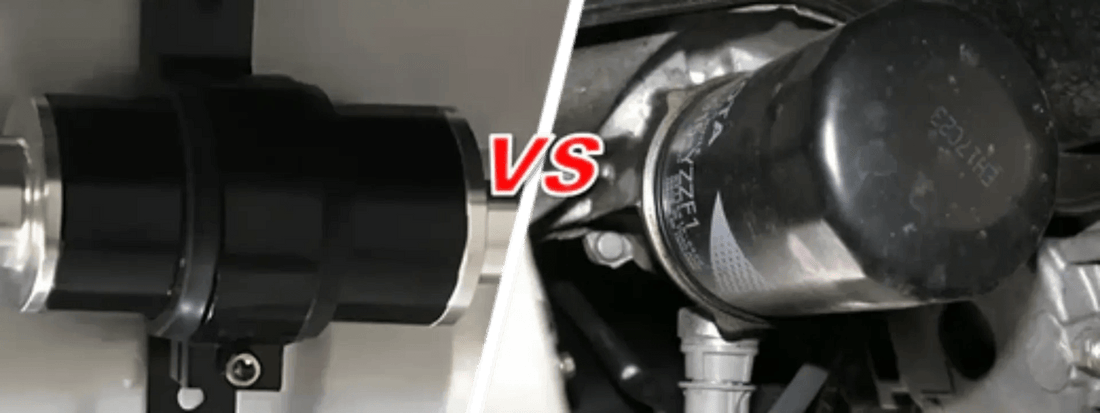
Fuel Filter vs. Oil Filter: Essential Differences You Must Know!
Have you ever been puzzled about the difference between a fuel filter and an oil filter? You're not the only one! Many vehicle owners and enthusiasts often mix up these two vital parts of an engine system. Although both are important for keeping the engine running smoothly, their functions, placements, and designs are quite different. Confusing them can result in significant problems, such as engine damage or decreased performance. In this detailed guide, we'll explore the unique functions of fuel filters and oil filters, highlighting their differences and the importance of proper maintenance.
A Brief Comparison Sheet
| Feature | Fuel Filter | Oil Filter |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Removes contaminants from fuel | Filters impurities from engine oil |
| Size | Generally smaller | Larger due to higher volume of oil |
| Location | Along the fuel line or in the tank | On or near the engine block |
| Design Complexity | Simple design | More complex, built to withstand higher pressures |
| Filtration Targets | Larger particles (1-10 microns) | Smaller particles (5-30 microns) |
| Replacement Frequency | Every 20,000-30,000 miles | Every oil change (3,000-7,500 miles) |
| Cost Range | $10 - $50 | $5 - $25 |
In This Post
- A Closer Look at Fuel Filters and Oil Filters
- What Does a Fuel Filter Do?
- What Is An Oil Filter?
- 7 Key Differences Between Fuel Filters and Oil Filters
- Can You Use an Oil Filter as a Fuel Filter?
- Maintenance Tips for Optimal Performance
- Don't Mix Up Fuel Filters and Oil Filters!
A Closer Look at Fuel Filters and Oil Filters
To appreciate the differences between fuel filters and oil filters, let's first take a closer look at what each component does.
What Does a Fuel Filter Do?
The fuel filter, as its name implies, plays a vital role in your vehicle's fuel system by removing contaminants and impurities before they can reach sensitive components like injectors and fuel pumps. Acting as a gatekeeper, it ensures that only clean fuel is delivered to the engine, protecting these critical parts from damage and contributing to better fuel efficiency and reduced emissions. Fuel filters are built to withstand the demanding conditions of the fuel system, which operates under high pressures and temperatures.
They typically feature robust metal housings or durable plastic casings that resist corrosion while maintaining structural integrity. Inside, pleated paper or synthetic media filters trap even the smallest particles, ensuring that the fuel remains as pure as possible for optimal combustion.

What Is An Oil Filter?
While the fuel filter safeguards the fuel system, the oil filter plays an equally crucial role in preserving the engine's integrity by protecting its lifeblood: the lubricating oil. As oil circulates through the intricate network of moving parts within the engine, it accumulates debris, metal shavings, and byproducts of combustion. Left unchecked, these contaminants can accelerate wear and tear, leading to premature engine failure.
Oil filters are designed to be robust and replaceable, often featuring a cylindrical metal casing with a removable bottom or top plate for easy access. Within this casing, a tightly wound paper or synthetic filter media is encased, providing a vast surface area for trapping contaminants as oil flows through.
7 Key Differences Between Fuel Filters and Oil Filters
Now that we've covered what each filter does, let's dive deeper into some key differences between them.
1. Functionality
The primary function of a fuel filter is to purify the fuel before it enters the engine. It ensures that only clean fuel reaches critical components like injectors or carburetors. In contrast, an oil filter cleans the engine oil as it circulates through the engine. This distinction is crucial; using one type of filter in place of another can lead to severe damage.
2. Size
Generally speaking, fuel filters tend to be smaller than oil filters. This size difference reflects their respective roles; since they deal with different fluids under different conditions, their dimensions vary accordingly. For instance, an inline fuel filter may be compact enough to fit within tight spaces along the fuel line.
3. Location
As mentioned earlier, fuel filters are typically found along the fuel line or within the fuel tank itself. In contrast, oil filters are usually located on or near the engine block for easy access during oil changes. Knowing where each filter is located can save you time and frustration when performing maintenance on your vehicle.

4. Design
Fuel filters often have a simpler design compared to oil filters. They usually consist of a housing that contains a filtering medium (like paper or mesh) designed to trap contaminants without significantly restricting fuel flow. Conversely, oil filters are more complex; they must withstand higher pressures and temperatures while effectively filtering out particles from thicker oil.
5. Filtration Targets
Fuel filters are specifically designed to remove impurities from gasoline or diesel, targeting larger particles like dirt and rust as well as smaller contaminants down to 1 to 10 microns, while oil filters focus on cleaning engine oil by capturing a wide range of contaminants, including dirt, metal shavings, and carbon deposits, typically targeting particles ranging from 5 to 30 microns in size.
6. Types of Oil Filter vs. Fuel Filter
Fuel filters come in various designs tailored for specific applications:
- Inline Fuel Filters: These are commonly used in modern vehicles due to their ease of access for maintenance. They effectively trap dirt and debris while allowing for sufficient flow rates.
- In-Tank Fuel Filters: Often part of the fuel pump assembly in modern vehicles, these filters provide an additional layer of filtration before fuel enters the lines leading to the engine.
- High-Efficiency Fuel Filters: Designed for performance engines or vehicles that use high-octane fuels, these filters offer superior filtration capabilities while maintaining high flow rates.
- Diesel Fuel Filters: These specialized filters are designed to handle water contamination and particulate matter specific to diesel fuels. They often include water separators to prevent water from entering the injection system.
Oil filters also come in several types tailored for different needs:
- Spin-On Oil Filters: The most common type found in many vehicles today; they are user-friendly and allow for quick changes during routine maintenance.
- Cartridge Oil Filters: More common in European vehicles; they require more effort during replacement but often offer better filtration due to their larger surface area.
- High-Performance Oil Filters: Designed for racing or high-performance applications; these filters provide enhanced flow rates and filtration capabilities under extreme conditions.
- Extended Life Oil Filters: Built with advanced materials that allow them to last longer between changes; ideal for drivers who prefer extended intervals between oil changes.
- Magnetic Oil Filters: These innovative designs use magnets to attract metal particles within the oil; while still requiring standard filtration media, they provide an additional layer of protection against wear.
Understanding these variations can help you choose the right filter for your vehicle's needs.
7. Replacement Frequency and Cost
Regular replacement of both filters is essential for optimal vehicle performance:
- Fuel Filters: It's usually recommended to replace these every 20,000 to 30,000 miles, or according to your owner's manual.
- Oil Filters: These should be changed every time you change your oil, which is generally every 3,000 to 7,500 miles, based on your vehicle.
Regarding costs:
- Fuel filters typically range from $10 to $50.
- Oil filters can vary from $5 to $25, depending on the brand and type.
Choosing quality filters can save you from costly repairs later on!
Can You Use an Oil Filter as a Fuel Filter?
Absolutely not! Attempting to use an oil filter as a fuel filter or vice versa can have devastating consequences for your engine. These components are designed specifically for their respective functions and are not interchangeable.
Using an oil filter as a fuel filter could result in fuel contamination, as the filter may not be able to effectively remove all impurities from the fuel. This could lead to issues like clogged fuel injectors, poor engine performance, and potentially even engine failure.
Conversely, using a fuel filter as an oil filter would be equally disastrous. Fuel filters are not designed to handle the high pressures and viscosity of engine oil, and they would quickly become overwhelmed, resulting in insufficient lubrication and catastrophic engine damage.
It's crucial to always use the correct filters for their intended purposes and follow the manufacturer's recommended replacement intervals. Neglecting to do so could result in costly repairs and potentially jeopardize the overall health and longevity of your vehicle's engine.
Maintenance Tips for Optimal Performance
To ensure your vehicle runs smoothly and efficiently:
- Regular Inspections: Check both your fuel and oil filters during routine maintenance checks.
- Follow Manufacturer Guidelines: Always adhere to your vehicle's owner manual regarding replacement intervals.
- Use Quality Parts: Invest in high-quality filters from reputable brands like EVIL ENERGY ; this will ensure better filtration and longer-lasting performance.
- Stay Informed About Symptoms: Be aware of signs that may indicate a clogged filter-such as reduced power during acceleration (for fuel filters) or unusual noises from the engine (for oil filters).
Don't Mix Up Fuel Filters and Oil Filters!
Understanding the distinction between fuel filters and oil filters is essential for any car owner aiming to maintain their vehicle's engine health. Each filter serves a unique purpose in the intricate workings of an engine, safeguarding it against contaminants that could lead to costly damage. Fuel filters act as vigilant guardians, ensuring only clean fuel reaches the engine, while oil filters protect the lifeblood of the engine by keeping the oil clean and free of debris. By prioritizing regular maintenance and timely replacements of these vital components, you not only enhance your vehicle's performance but also prolong its lifespan, ensuring a smooth ride for years to come.


![EVIL ENERGY 4/6/8/10AN PTFE Fuel Line Kit | E85 Nylon Braided Hose | 16/20FT Black Black with Comprehensive Fittings [20FT]](http://www.ievilenergy.com/cdn/shop/files/Test-2025-Evilenergy-125598065_165x.png?v=1742144807)
![ptfe hose fitting kit [16FT]](http://www.ievilenergy.com/cdn/shop/files/Test-2025-Evilenergy-125598171_165x.png?v=1742144807)
![CPE Fuel Line[25FT]](http://www.ievilenergy.com/cdn/shop/files/25FTCPE_FuelLine_165x.png?v=1735220649)
![CPE Fuel Line[20FT]](http://www.ievilenergy.com/cdn/shop/files/20FTCPE_FuelLine_165x.png?v=1735220649)